CFDs, known as contracts-for-differences, is an advanced trading strategy where an agreement is struck between a trader and brokerage in the financial derivates trading market. Trade settlements are cash-settled as a resulting difference between the open and closing trade prices while there is no delivery of securities or physical goods through contracts-for-differences.
CFDs authorize traders the ability to trade the fluctuating price movements exhibited in securities and derivatives. Derivatives can be defined as financial instruments whose value is determined from an underlying asset. Traders primarily trade by predicting whether the value of a security or underlying asset (derivative) will appreciate or depreciate.
The net difference generated as a result of a trader’s gain or loss is cash-settled through an investor’s brokerage account. CFDs trading is conducted through over-the-counter markets where the tradable contract exists between the broker and client.
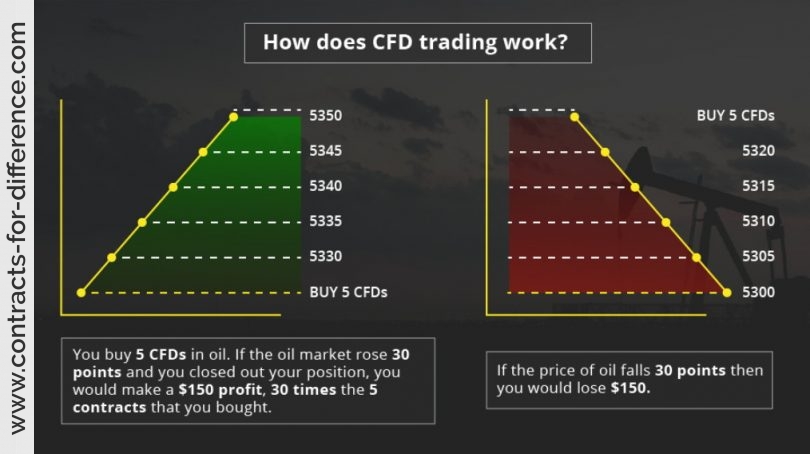
Traders who trade contracts-for-difference can maximize the benefits of owning a security without truly owning it or having to worry about the physical delivery of an asset. Less regulatory oversight and rules monitor the contracts-for-differences market enabling traders to start with smaller investment sums while CFDs are traded on margin.
Standard margin requirements set forth by contracts-for-difference brokers range between 2% to 20% while CFDs generally yield high leverage which can result in the potential for more significant returns or losses for a trader.
CFDs are not exceedingly regulated while a broker’s credibility is vastly determined upon its financial transparency and reputation. Due to contracts for differences lack of regulatory oversight, contracts-for-difference options are not allowed in the United States while underlying assets have been reported to reflect acute volatility.
Should erratic volatility continue significant spreads between CFDs bid and ask prices can result which moderately impair a trader’s ability to execute upon small market fluctuations occurring in the CFD market.
While CFDs provide traders with the ability to trade ETFs, commodity futures, and stock indices the magnification of losses that can result from the incorrect use of leverage may be severe despite a trader’s ability to execute long or short positions.