
GDPR and Its Impact. The Internet has changed the way we communicate, operate and execute tasks. We as a customer, client, businessman etc. send emails, share documents, pay bills and purchase goods online by entering our personal details. But is this personal information or data secure? In this new online world, the free user seems to have become the product. Giant Internet companies like Facebook, Google and others have been monetizing data as their primary revenue model.
A small set of users has increasingly pushed back against this mass data collection about the user’s private lives and browsing habits and this has finally led to governments waking up. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the new data protection regulation from the EU. The European Parliament embraced GDPR in April 2016, superseding an outdated data protection directive from 1995 and it came into effect on May 25, 2018. GDPR is applicable to all businesses and organizations selling to and storing personal information on citizens in Europe, irrespective of whether the data processing takes place in the EU or not.
GDPR is likely to apply to all organizations in the world that control or process personal data of EU residents. The regulation is focused on the “protection of personal data”, not merely the privacy of personal data.
It is intended to strengthen and unify data protection for individuals within the EU.
Impact of GDPR
GDPR is an extensive data privacy policy that exerts influence on businesses established worldwide.
Within hours of the implementation of EU GDPR, technology giants Google and Facebook have been hit with privacy complaints that could carry the penalty of up to $8.15 billion in total.
As per Goldman Sachs report April 2018, Facebook earned 24% of its global revenue from EU and could suffer a negative impact of up to 7% because of GDPR.
According to the report of Consult Hyperion, the financial impact of GDPR could be as high as €4.7 billion in fines for EU banks within three years of the regulations being introduced. The study predicted that financial institutions operating in the EU could experience 384 data breaches during the three-year period after May 2018.
As per the research of Ministry of Justice, the cost to UK business could rise by as high as £320 million a year, and £2.1 billion over fourteen years.
It is important for an enterprise to notify the authority within 72 hours about a data breach that they have detected, and if they fail to inform the affected victims about it, then an enterprise can be fined with huge penalties.
In the UK, the recorded highest fine for a data breach was levied on the telecommunications company Talk Talk, which was fined for their violation of data over 150,000 customers. In this instance, the cost to the telecommunications company was £400,000. The company lost 101,000 customers and suffered non-fine related costs of £60 million.
Significant Fines for Non-Compliance
Organizations established anywhere in the world involved in collecting or processing personal data on EU residents must abide by the GDPR regulation, or they will face remarkable financial penalties and reputational damage.
Penalties for companies and organizations will be at 4% of annual global revenue or 20 million Euros whichever is greater.
Conclusion
Data is the new oil.
No doubt GDPR pose many challenges but also creates vast opportunities for businesses which are ready to be nimble. Companies engaged in securing individual’s privacy and are transparent about how the data is being used, will be able to build deeper trust and retain more customers.




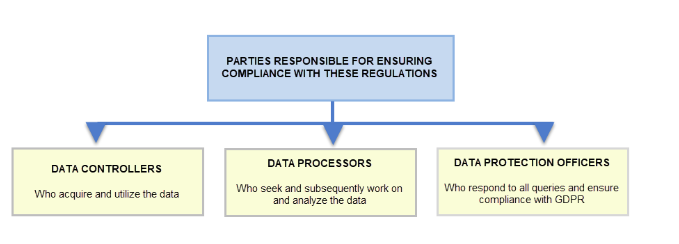












Good post on GDPR